Advances in accelerator technology and in the theoretical understanding of collective instabilities and production of coherent radiation, have been the driving forces of the progress toward brighter synchrotron radiation sources, with scientific applications developing in response to the availability of new sources. The rate of improvement in source capability has been tremendous: for 30 years x-ray source brightness has been increasing exponentially with a doubling time of about 10 months. A modern synchrotron source is eleven orders of magnitude brighter than a 1960s laboratory x-ray source. Seldom, if ever, in history (perhaps only in the field of visible laser optics and colliders for high energy physics) has a scientific discipline seen its tools change so dramatically within the active life of a single generation of scientists.
Approximately 1,700 scientists visit SSRL annually to conduct experiments in broad disciplines including life sciences, materials, environmental science, and accelerator physics. Science highlights featured here and in our monthly newsletter, Headlines, increase the visibility of user science as well as the important contribution of SSRL in facilitating basic and applied scientific research. Many of these scientific highlights have been included in reports to funding agencies and have been picked up by other media. Users are strongly encouraged to contact us when exciting results are about to be published. We can work with users and the SLAC Office of Communication to develop the story and to communicate user research findings to a much broader audience. Visit SSRL Publications for a list of the hundreds of SSRL-related scientific papers published annually. Contact us to add your most recent publications to this collection.
The Rocky Flats Environmental Technology Site (RFETS) is an environmental cleanup site located about 16 miles northwest of downtown Denver (Fig 1). Two decades of routine monitoring have shown that the environment around RFETS is contaminated with actinide elements (U, Pu, Am) from site operations, [1] and RFETS has been designated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) as a Superfund cleanup site. Until December 1989, the Rocky Flats Plant made components for nuclear weapons using various radioactive and hazardous materials, including plutonium, uranium and beryllium. Nearly 40 years of nuclear weapons production left behind a legacy of contaminated facilities, soils, and ground water. More than 2.5 million people live within a 50 mile radius of the site; 300,000 of those live in the Rocky Flats watershed.
Anthrax Toxin is a major virulence factor in the infectious disease, Anthrax (1). This toxin is produced by Bacillus anthracis, which is an encapsulated, spore-forming, rod-shaped bacterium. Inhalation anthrax, the most deadly form, is contracted through breathing spores. Once spores germinate within cells of the immune system called macrophages (2), bacterial cells are released into the bloodstream. There they proliferate rapidly and secrete Anthrax Toxin, ultimately leading to septic shock and death. Although antibiotics may be used to kill the bacteria, the level of toxin has often become so high in the bloodstream that removing the bacteria alone is not sufficient to prevent death.
When we think of chlorine, we often relate it to the salt used in food preparation, chloride in the oceans, chlorine gas from swimming pools, and gaseous chlorofluorocarbons that have close links to the depletion of stratospheric ozone. We rarely think of thousands of chlorinated hydrocarbons that exist in the natural systems, several of which are highly toxic to humans (1). The C-Cl bond, common to all organo-Cl compounds, is strong and gives high stability to organo-Cl compounds. For this reason, several organo-Cl compounds have been synthesized and used extensively for years in agricultural and industrial applications.
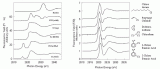
The famous 17th-century Swedish warship Vasa has been on display in the Vasa Museum since 1990 (Figure 1). The Vasa sank on its maiden voyage in 1628, and was recovered in 1961 after 333 years in the cold brackish water of Stockholm harbor. After extensive conservation treatment, the oaken Vasa appeared in good condition (1). However, high acidity and a rapid spread of sulfate salts and elemental sulfur were recently observed on many wooden surfaces. A research team led by Prof. Magnus Sandström, University of Stockholm, have approached the problem by using X-ray absorption near edge spectroscopy (XANES) at the sulfur K-edge.
Sulfur is essential for all life, but it plays a particularly central role in the metabolism of many anaerobic microorganisms. Prominent among these are the sulfide-oxidizing bacteria that oxidize sulfide (S2-) to sulfate (SO42-). Many of these organisms can store elemental sulfur (S0) in "globules" for use when food is in short supply (Fig. 1). The chemical nature of the sulfur in these globules has been an enigma since they were first described as far back as 1887 (1); all known forms (or allotropes) of elemental sulfur are solid at room temperature, but globule sulfur has been described as "liquid", and it apparently has a low density – 1.3 compared to 2.1 for the common yellow allotrope α-sulfur.
Computer hard drives and other advanced electronic devices depend on layered stacks of magnetic and non-magnetic materials, but researchers don't fully understand why such layered materials exhibit new properties that cannot be predicted from the properties of the individual layers. In a recent publication a team working at SSRL and the ALS describes new methods, based on x-ray spectroscopy and x-ray microscopy, that reveal the magnetic structures at the boundaries between these layers. Their data show that the boundaries are not as clean as previously assumed but a new ultrathin interface layer may be formed by a chemical reaction. The thickness of the interfacial layer is found to change with temperature and this change can be directly correlated with the magnetic properties of the multilayer stack. The work provides the first magnetic images of a buried interface and gives direct experimental evidence for the existence and long-assumed importance of interfacial magnetic spins.
Sorption reactions on particle surfaces can dramatically affect the speciation, cycling and bioavailability of essential micronutrients (i.e. PO43-, Cu, Zn etc.) and toxic metals and metalloids (i.e. Pb, Hg, Se, As) in soils and aquatic environments. Considerable attention has been focused on understanding metal sorption reactions at a molecular/mechanistic level and the effects of metal concentration, pH, ionic strength, and complexing ligands on the ways in which metal ions bind to the surfaces of common mineral phases such as Fe-, Mn- and Al-(hydr)oxides and clays. However, a significant fraction of mineral surfaces in natural environments are extensively colonized by microbial organisms, which can also be potent sorbents for metals due to the large number of reactive functional groups that decorate the cell walls and outer membranes of bacterial surfaces.
The strong electron correlations in transition metal oxides give rise to such phenomena as high-temperature superconductivity in layered cuprates and to stripe-like order in layered cuprates and nickelates. In the case of the manganites, an additional strong electron-lattice interaction leads to a very rich phase diagram in which structural, magnetic, and transport properties are intimately related. Colossal magnetoresistance (CMR) has been observed in the perovskite and double-layer manganites, but not in the single-layer system La1-xSr1+xMnO4 (Mn214).
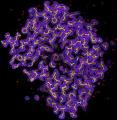
Protein crystallography can routinely determine the 3D structure of protein molecules at near atomic or atomic resolution. The bottleneck of this methodology is to obtain sizable and good quality protein crystals. Overcoming the crystallization difficulty requires the development of the new methodologies. One approach is to use NMR to image protein molecules in solvent. However, it is only applicable primarily to macromolecules in the lower molecular weight range. Another approach under rapid development is single molecule imaging using cryo electron microscopy (cryo-EM). The highest resolution currently achievable by this technique is ~ 7 Å for highly symmetrical viruses (1) and 11.5 Å for the asymmetrical ribosome (2). The main limitations to achieving better resolution by cryo-EM are radiation damage, specimen movement and low contrast.