Overview
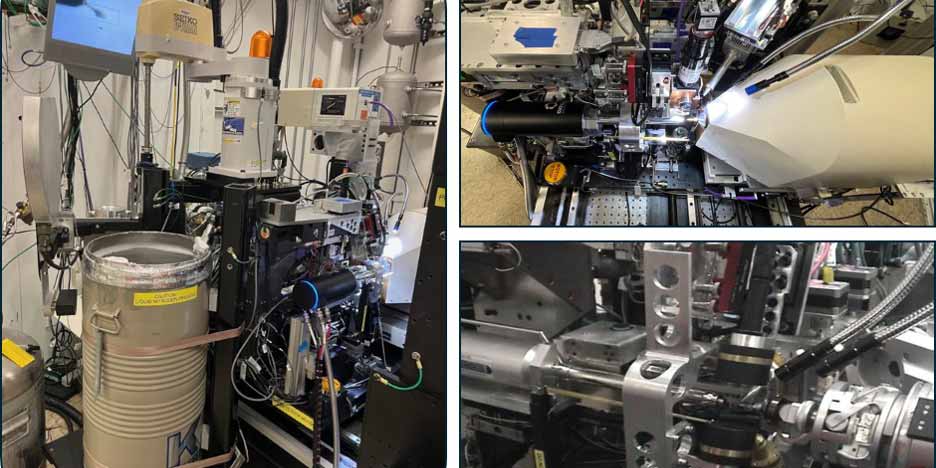
BL 9-2 is a broad-fan wiggler end station dedicated for monochromatic, high-throughput and high-resolution macromolecular crystallography experiments. Optimized for SAD and MAD experiments, BL9-2 can be run in a full remote access mode and features a remote access-controlled UV-Vis microspectrophotometer for in-situ single crystal absorption spectroscopy measurements.
BL9-2 employs a 16-pole, 2-Tesla wiggler with a peak critical energy at 12 KeV, a vertically collimating Rh-coated Si mirror, and a double-crystal Si(111) monochromator with a ~0.01% energy bandpass producing ~6x1011 p/s at the Se edge with a full energy range of 6-14 KeV. A vertically and horizontally focusing toroid mirror produces a beam focus of 70 x100 um2. BL9-2 is equipped with an Eiger X 16M pixel array detector with a readout speed of up to 100 Hz which enables rapid high-redundancy diffraction experiments, and the use of low-dose high-speed x-ray raster searches to locate smaller crystals.
Features and Techniques
Remote Access Crystallography - Users control and carry out their crystallography experiments and run processing software in real time from anywhere in the world. This is accomplished with a simple free app that runs on the user's remote computer which connects to a server running at SSRL.
Single Crystal UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopy – Single crystal UV-Vis spectra can be collected in-situ from samples mounted on the goniometer as a function of time or dose. These measurements can be used to monitor radiation damage, confirm an oxidation state of a metal, or track a reaction in-crystallo.
Large Unit Cells - Diffraction from very large unit cells (for example, viruses and large complexes) can be resolved with pixel array detectors (PADs). They have large detection areas and can be placed long distances from the sample, and they have excellent intrinsic resolving power and no pixel crosstalk.
Automated Screening - Samples are systematically mounted from a frozen cassette using a robot and subsequently aligned, exposed, indexed, and assigned a score for overall diffraction quality.
X-ray Rastering - Low-dose X-rays are used to accurately locate visually obscured crystals in loops and other mounts, or to identify areas of a crystal that have improved diffraction.
MAD/SAD Phasing - Multi- and single wavelength anomalous diffraction (MAD and SAD, respectively) is used to solve the phase problem in structure determination. Accurate heavy atom absorption edge spectra provide the most useful energies (f' and f") for MAD data collection. High-speed ultra-redundant data collection can be used to obtain significant signal from weak anomalous scattering atoms such as sulfur.
Metal Identification – Excitation scans are useful to quickly determine the heavy element content in crystals. The excitation scan measures the fluorescence counts from any element present in the sample with an absorption edge below the excitation energy. Excitation scans take less time than the MAD scans and thus are a faster way to determine the presence of a heavy atom derivative/ligand in the sample.
Source: 16-pole, 2-Tesla wide-fan wiggler.
For more information on the features of BL9-1, see the Macromolecular Crystallography Website: Macromolecular Crystallography
Status —
Source —
Instrumentation —
| Sample Exchange Robot | SSRL Stanford Auto-Mounter Compatible Containers: SSRL Cassettes, and Uni-pucks Compatible Sample Pins: Hampton-style (magnetic and copper magnetic, ALS, SPINE and MiTeGen |
|---|---|
| In-situ UV-Vis Spectrometer | deuterium and halogen lamps provide a 40 um2 light spot by default, single crystal absorption (default) and fluorescence configurations are available |
| Goniometer | SSRL Single-axis micro-diffractometer, air bearing, +/-0.61.5 um SOC |
| Detector | Dectris Eiger X 16M pixel array detector: frame rate up to 20 Hz, count rate: ~107, pixel size: 75 um2, active area: 311 x 328 mm2. |
| Energy Spectrometer | Hitachi Vortex-90EX Silicon Drift Detector is used for automated energy and excitation scans. |
Sample Environment —
| Cryogenic to Elevated Temperature | Axial cryostream range: 100 - 370 K, remote controllable |
|---|---|
| Non-cryogenic Temperature and Humidity Control | Adjustable humidity stream 30.0 % to 99.5 % ±0.05 % |
| High Voltage Electric Field | 0-2 kV source |
Publications
Publications
Highlights
Science Highlights
We are in the process of porting over science highlights from our previous system. You can access new highlights and a portion or our catalog here.
For science highlights dated before 2021 visit this site. Use the filters to narrow down your search by year and beam line.