When a blood vessel is injured, a repair mechanism is initiated through the formation of a hemostatic plug that seals the wound to prevent blood loss. This life saving process becomes life threatening when clots form inside a functional blood vessel leading to pathological thrombosis. Therefore, the clotting process must be carefully regulated. Arrest of bleeding is achieved through platelet adhesion and thrombin-related fibrin clotting at the site of injury. In order for the platelets to stick to the injured tissues and to each other, they need to be activated. In addition to causing fibrin clotting, the protease thrombin plays a crucial role in activating platelets and its action is tightly regulated because of its procoagulant and anticoagulant activities (Dahlback, 2000). Therefore, the molecular details of the interaction of thrombin with platelets are required for a proper understanding of the clotting process.
Most platelet responses to thrombin depend on protease-activated receptors (PARs), which are seven-transmembrane-spanning G protein-coupled receptors expressed at the platelet surface (Sambrano, 2001, Sadler, 2003). Glycoprotein Iba (GP Iba) in the GpIb-IX-V receptor complex is the major binding site for thrombin associated with platelets. We have successfully crystallized complex with the N-terminal domain of GP Ibato a resolution of 2.3 Å. The data sets were collected at SSRL using Beam Line 9-2. The structural studies provide insights into the modulation of thrombin function (Celikel et al., 2003).
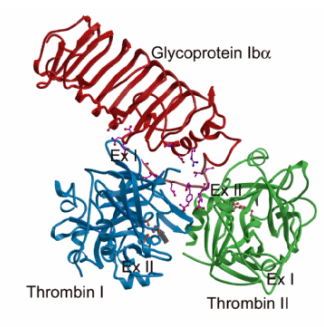
Thrombin has two positively charged patches located on opposite ends of the molecule called exosite I and exosite II. These sites are distinct from the catalytic center. Conflicting reports have previously appeared in literature, some concluding that GP Iba binds through exosite I and others favoring exosite II. Our structural studies show that thrombin uses both exosite I and exosite II for GP Iba binding. In the crystal structure (Fig. 1), one GP Ibabinds to two thrombin molecules through exosite I and exosite II where the two thrombin molecules come together to form a dimer (Celikel et al., 2003).
We hypothesize that the initial contact of GP Iba occurs through the exosite II of a-thrombin and involves negatively charged residues in GP Iba including the sulfated Tyr276 and Asp277. The first interaction paves the way for the interaction at the exosite I, probably through proper orientation of certain residues and through thrombin:thrombin interactions. The dual mode interaction observed in the current structure has the potential to mediate receptor clustering on the platelet surface, thus promoting signaling and activation. In addition to this, the dual mode interaction would also limit the prothrombotic function of a-thrombin by reducing its fibrinogen clotting activity through the blockage of exosite I. Therefore, GP Iba may be an important player in the maintenance of a proper hemostatic balance after a-thrombin generation at sites of vascular injury.
- Dahlback, B. (2000) Blood Coagulation. Lancet 355, 1627-1632
- Sambrano, G. R., Weiss E. J., Zheng Y.-W., Huang W., and Coughlin S. R. (2001) Role of Thrombin Signalling in Platelets in Haemostasis and Thrombosis. Nature 413, 74-78.
- Sadler, E. J. (2003) A Menage a Trois in Two Configurations. Science 301, 177-179
- Celikel, R., McClintock, R. A., Roberts, J. R., Mendolicchio, G. L., Ware, J., Varughese, K. I., and Ruggeri, Z. M. (2003) Modulation of a-Thrombin Function by Distinct Interactions with Platelet Glycoprotein Ib. Science 301, 218-221
Celikel, R., McClintock, R. A., Roberts, J. R., Mendolicchio, G. L., Ware, J., Varughese, K. I., and Ruggeri, Z. M. (2003) Modulation of a-Thrombin Function by Distinct Interactions with Platelet Glycoprotein Ib. Science 301, 218-221




