:: X-ray Reflectivity
:: Grazing
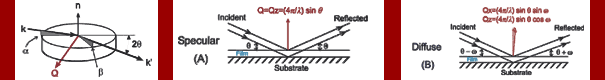
Incidence X-ray Scattering and Diffraction on Thin Films
:: Surface
Diffraction
:: Small Angle X-ray
Scattering for Materials Science
::Home
Small Angle X-ray Scattering for Materials Science
Introduction
Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) is a well-established characterization
method for microstructure investigations in various materials. It can probe
structural inhomogeneities (really electron density differences) from the
near atomic scale (1nm) to the micron scale (1000nm). The method involves
measuring the scattered X-ray intensity as a function (typically small)
scattering angle angles and is generally performed in transmission. SAXS
is used to characterize the size scale of inhomogeneities (e.g, pores, inclusions,
second phase regions) in polymer blends, microemulsions, geological materials,
bones, cements and ceramics.
Instrumentation
SAXS measurements can be done at either beamlines 1-4
or 4-2.
Beamline 7-2
can also be used for certain SAXS experiments, such as anomalous SAXS. There
is also a now ultra small angle (uSAXS) facility on 4-2,
for measurements of Q to below 0.0001 Å-1.
Analysis
Some details on data reduction can be found here
(see new developments link). In general SAXS analysis is model dependent,
and will, in general, depend on the material under investigation (e.g.,
degree of order, nature of the inhomogeneities, concentration of the inhomogeneities).
Some details can be found here
and in the references below.
Recently, we have developed a novel method of analyzing SAXS data from random or suitably disordered two-phase materials {Hedstrom].
Applications of SAXS
for materials science
An application
of SAXS on beamline 1-4
shows how to tailor plastics at a molecular level to improve manufacturability
of these materials.
SAXS has been used
to determine the morphology of highly porous thin films, using a novel
analysis method. Representative morphologies as a function of porosity
are shown in the figure below. Details are given here; contact Mike
Toney for more information.
Further General Reading:
|
||
Content Owner: Mike Toney |
Page Editor:
Nik Stojanovic |
Page Last Updated: 28 Jun 2010 18:02 PDT |