 Tumour necrosis factor is a polypeptide cytokine involved in inflammation and
the acute phase response. TNF-alpha is present in larger quantities in persons
with rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn's disease. Direct inhibition of
TNF-a by
the commercial biological agents etanercept (Enbrel), infliximab (Remicade),
adalimumab (Humira), has produced significant advances in rheumatoid arthritis
treatment and validated the extra-cellular inhibition of this proinflammatory
cytokine as an effective therapy. However, despite considerable incentives,
viable leads for analogous small-molecule inhibitors of
TNF-a have not been
reported (1). Such drugs with attendant advantages in manufacturing, patient
accessibility, administration, and compliance would represent a major advance
in the treatment of TNF-a mediated diseases.
Tumour necrosis factor is a polypeptide cytokine involved in inflammation and
the acute phase response. TNF-alpha is present in larger quantities in persons
with rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn's disease. Direct inhibition of
TNF-a by
the commercial biological agents etanercept (Enbrel), infliximab (Remicade),
adalimumab (Humira), has produced significant advances in rheumatoid arthritis
treatment and validated the extra-cellular inhibition of this proinflammatory
cytokine as an effective therapy. However, despite considerable incentives,
viable leads for analogous small-molecule inhibitors of
TNF-a have not been
reported (1). Such drugs with attendant advantages in manufacturing, patient
accessibility, administration, and compliance would represent a major advance
in the treatment of TNF-a mediated diseases.
A group of Scientists at Sunesis Pharmaceuticals described a small molecule
TNF-a inhibitor initially identified from an in
vitro screen for compounds capable of disrupting TNF binding to TNF
receptor R1. By using the x-ray
diffraction data collected at beam line 7-1 at SSRL, He M.M. et al
were able to determine a co-crystal structure of TNF-a with the small molecule inhibitor.
The structure revealed a novel interaction in which one of the subunits of the
TNF-a trimer is replaced by the small molecule
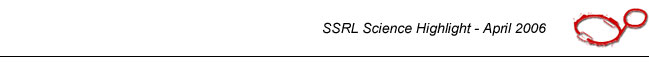
(Fig. 1A). The resulting TNF-a
dimer retained the same basic structural subunit fold as in the native trimer
but the angle between the subunits within the dimer was slightly widened. The
compound binds in the hydrophobic core of the protein that was completely
buried within the subunit interfaces in the intact
TNF-a trimer crystal
structure. Interestingly, a large fraction of the contact surface with the
small molecule involves six tyrosine residues from the
TNF-a dimer (Fig. 1B).
Further biophysical experiments conducted at biologically relevant
TNF-a
concentrations confirmed that the compound was capable of dissociating
TNF-a
trimer in solution and that the compound interacts with intact
TNF-a trimer to
dramatically accelerate subunit dissociation.
Figure 1 Unusual inhibition mechanism of a small-molecule antagonist of the
trimeric cytokine TNF-a.
(A) X-ray co-crystal structure of the inhibitor
bound to TNF-a, superimposed on the structure of
the native TNF-a trimer
(shown in gray). The co-crystal structure (represented by the blue and yellow
monomers) shows that the antagonist binds in the hydrophobic core of the
protein, displacing one of the TNF-a subunits.
(B) Much of the 330-Å2 contact
area between the protein and the small-molecule antagonist is contributed by
six tyrosine residues, three from each protein subunit.
The results we have described should enable the design of appropriate assays
that may allow for the identification of potent small-molecule inhibitors that
inactivate multimeric proteins via a rapid predissociation-independent subunit
dissociation process.
Primary Citation
He, M.M., Smith, A.S., Oslob, J.D., Flanagan, W.M., Braisted, A.C., Whitty, A.,
Cancilla, M.T., Wang, J., Lugovskoy, A.A., Yoburn, J.C., Fung, A.D.,
Farrington, G., Eldredge, J.K., Day, E.S., Cruz, L.A., Cachero, T.G., Miller,
S.K., Friedman, J.E., Choong, I.C., Cunningham, B.C. Small-molecule inhibition
of TNF-alpha. Science v310 pp.1022-1025, 2005
References
| SSRL is supported by the Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences. The SSRL Structural Molecular Biology Program is supported by the Department of Energy, Office of Biological and Environmental Research, and by the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Research Resources, Biomedical Technology Program, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. |