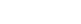The transition metal oxides exhibit a wide range of interesting properties, of which superconductivity in the copper oxides and colossal magnetoresistance in the manganese oxides are perhaps the best known. However, the strange magnetic behavior of several cobalt oxides is another example of these unusual properties, although not yet as intensively studied. The cobaltite system La1-xSrxCoO3 (LSCO) has a rich temperature-concentration phase diagram with anti-ferromagnetism and insulating behavior at low Sr concentrations, and ferromagnetism and metallic behavior at higher concentrations. The magnetism for the end compound LaCoO3 (LCO) is particularly unusual; it has no Co spin magnetic moment at low T (and is diamagnetic). As T increases from 4K, the magnetic susceptibility increases dramatically up to roughly 100K, and then decreases as T is increased to 300K. This behavior has been attributed to Co+3 having several different spin configurations. Initially only two were considered, a low spin state (LS, S=0) that is not magnetic and a high spin state (HS, S=2) that is strongly magnetic. In the '90s a third, intermediate spin configuration (IS, S=1) was proposed by Potze, et al. and Korotin, et al; this configuration should result in a distortion of the CoO6 octahedra (called a Jahn-Teller (JT) distortion). In the late '90s, Louca et al. reported neutron PDF results indicating a distorted Co-O environment, comparable to the Mn-O distortions observed in the similar manganite systems La1-yCayMnO3 (LCMO) and La1-zSrzMnO3 (LSMO). However, to date, these neutron PDF data for the cobaltites are the only structural results that support a JT distortion. While some recent experimental results are argued to be consistent with a large Co-O JT distortion and its associated IS state, many others appear to be inconsistent with such an interpretation. Our group at UC Santa Cruz, therefore took a closer look at the possibility of a JT distortion of the CoO6 octahedra, using a combination of the EXAFS and neutron PDF techniques; here we focus on the Co K-edge EXAFS results, for data collected at SSRL.
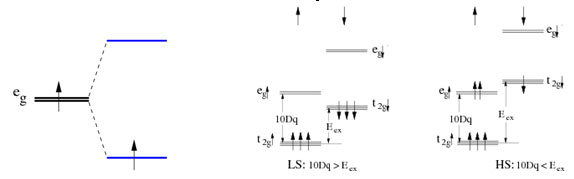
Before discussing Co, we first discuss three important energies that determine the ordering of the energy levels, and hence the spin configuration. For the free atom the 3d spatial states form a 5-fold degenerate multiplet, but in a cubic crystal field, these states are split into 2-fold degenerate eg and 3-fold degenerate t2g multiplets, with a splitting energy called 10Dq. The second important energy is called the exchange energy, Eex, which is roughly the energy to add a spin-down electron to a state that is occupied by a spin-up electron. The third energy comes from the Jahn-Teller (JT) interaction when there is only one eg electron present. Then a local distortions about the Co ion, such as two long Co-O bonds and four short Co-O bonds, will split the eg states (one state decreases in energy and the other increases), and the electron can go to the lower energy state if this distortion takes place - See Fig 1. Note that the total energy is not lowered if two eg electrons are present. The distortion does cost a small strain energy, but for eg states the net energy is lowered and the crystal locally spontaneously distorts. When the energies 10Dq and Eex are comparable, a tiny change in energy could change the system from high spin to low spin (See Fig. 1) - and for one possible set of energy levels (10Dq ~ Eex), including a JT distortion can lead to the intermediate spin state.
For LCO, with six 3d electrons on Co, the filled energy states for the three localized spin state models are: 1) LS - t2g6eg0, with no eg electrons and all six t2g spins paired (observed at low T); 2) HS - t2g4eg2, expected at high T, note that with two eg electrons it is not JT active; and 3) IS - t2g5eg1, - with one eg electron it should be JT active, creating Co-O bonds of different lengths in the lattice. Thus a significant JT distortion is a signature for the IS state; if such a distortion is observed, then the IS state must be included in modeling the magnetism; however, if no JT distortion is present, no localized states containing one eg electron exist and the IS state should not be important.
![s2(T) for La0.8Sr0.2CoO3 samples from two sample makers [MZ (solid squares) and NS (open squares)], as well as the correlated Debye fits (dashed line for MZ and solid line for NS samples). The data overlap very well within the errors. The corresponding data for a La0.78Ca0.22MnO3 sample (Mn-O bond), using the same technique, are replotted here with open circles; this sample has a large JT distortion that develops between 100 and 200 K. Figure 3.](/content/sites/default/files/images/science/highlights/2009/cobaltite_sys_fig3.jpg)
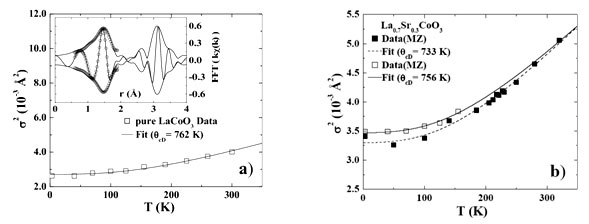
Temperature dependent (4 - 330K) EXAFS transmission Co K-edge data were collected at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL) for powdered LSCO samples over a range of Sr concentrations, x = 0.0-0.3. A standard data reduction (RSXAP) package was used to extract the EXAFS spectra which were fit in r-space to theoretical EXAFS functions generated by FEFF 8.20. Our primary interest here is s, the width of the Co-O pair distribution function, which parameterizes the amount of variation present in the lengths of the Co-O bonds; the results are generally plotted as s2 vs T. There are several contributions to s2(T) for the Co-O bond, thermal vibrations (or phonons), possibly some small static disorder from doping, and a JT distortion if it is present. Note that different contributions to s2 add up in quadrature if their mechanisms are uncorrelated; i.e. s2= s2static + s2phonons + s2Jahn-Teller. If no JT distortions are present, the s2(T) data can be fit to the correlated Debye model plus a static offset; this model is usually a good approximation for all phonon modes including acoustic and optical phonons. The thermal phonon contributions were determined from a fit of s2 vs. T, for 4 ≤ T ≤ 330 K.
Figure 2 shows s2(T) (Co-O peak) for x = 0.0 and 0.3; there is no evidence for a step in s2(T), or any significant excess static distortion at low T that would indicate any JT effect. The inset shows a fit of the Co-O peak. In Fig. 3, we plot similar s2(T) data and the correlated Debye fits for two different La0.8Sr0.2CoO3 samples (designated MZ and NS). We also plot, for comparison, corresponding results for a 22% Ca-doped LCMO sample which has a metal-insulator transition around 190 K associated with a significant Jahn-Teller distortion of the MnO6 octahedra. Between 100 and 200 K, a JT splitting develops, with two longer Mn-O bonds and four relatively shorter bonds for some sites (at low T, the Mn-O octahedron has six bonds of nearly equal length). The proposed JT distortion of the Co-O bonds in LSCO is of comparable magnitude to that observed in LCMO. However, the lack of any significant step for LSCO in Figs. 2 and 3 and the rather small static distortion at 4K (≤ 0.0006 Å2) means that there is very little JT distortion of the Co-O PDF peak between 4 and 300 K for the 20% Sr doped LSCO samples. One cannot, of course, rule out the possibility of a few percent of sites having a JT distortion. Together these results show no evidence for a significant fraction of the Co having a JT distortion and hence strongly question the presence of the proposed intermediate spin state. Our neutron PDF data also show no evidence for a JT distortion in LCO or LSCO, in complete agreement with the EXAFS results described above.
"Local Structure of La1-xSrxCoO3 Determined from EXAFS and Neutron Pair Distribution Function Studies", N. Sundarum, Y. Jiang, I.E. Anderson, D.P. Belanger, C.H. Booth, F. Bridges, J.F. Mitchell, Th. Proffen, and H. Zheng, PRL 102, 026401, (2009)